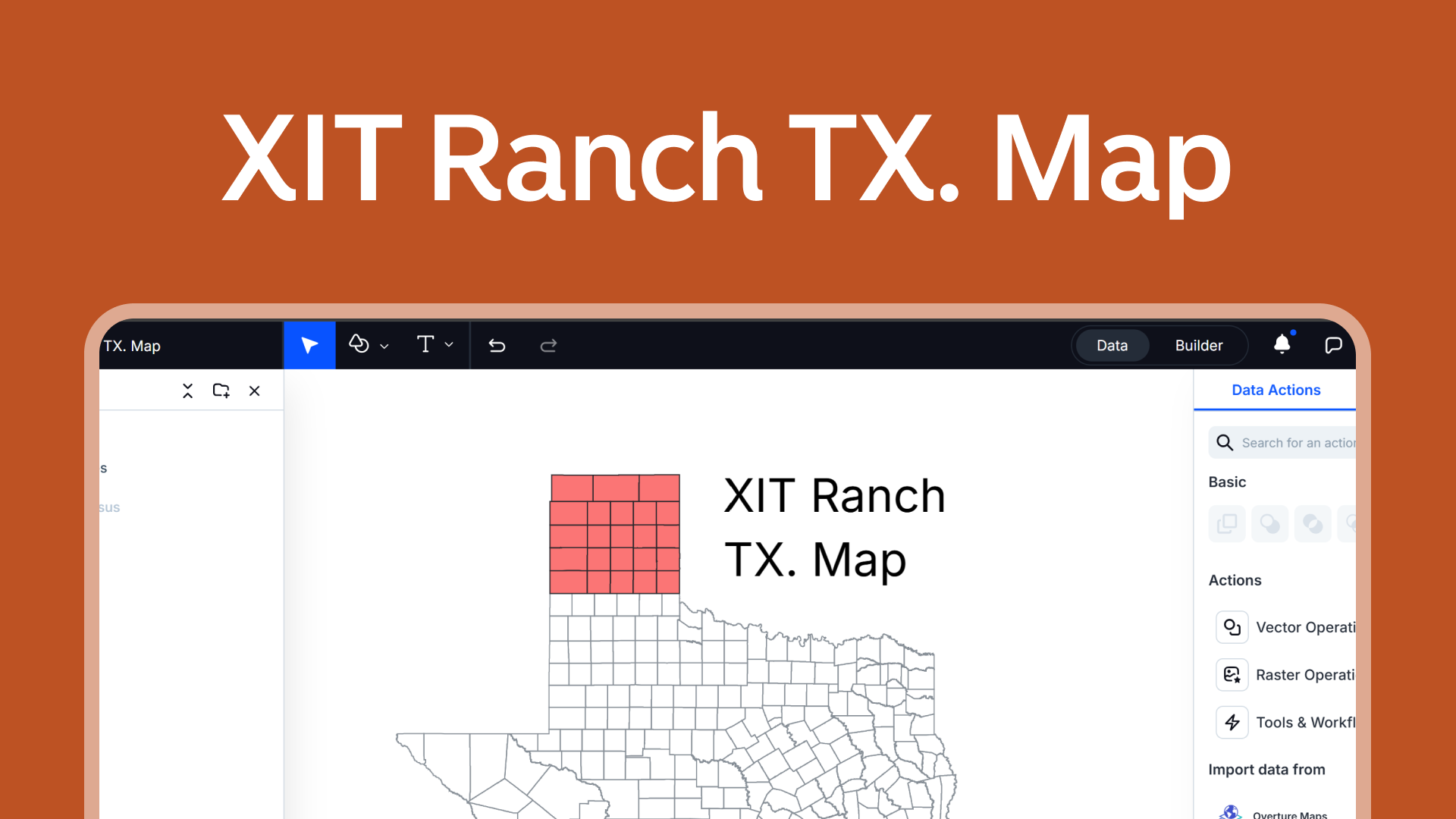
Creating a map is a useful skill that can help you see and understand information about different places. With Atlas, a browser-based platform, you can make detailed and interactive maps easily.
Here’s a simple guide to help you create a map using Atlas.
Step 1: Gather Your Data
Before you start making a map, gather the necessary data.
Your data might include points (such as locations of schools or businesses), lines (such as roads or rivers), and polygons (such as city boundaries or parks). Ensure your data is in a compatible format like CSV, Excel, or GeoJSON.
Step 2: Log in to Atlas
Open your web browser and navigate to the Atlas platform. Log in to your account or create one if you don’t have an account yet.
Step 3: Upload Your Data
- Navigate to the Add Data Section: In Atlas, find the section where you can upload your data in the top left corner.
- Upload Files: Upload your data files. Ensure each file is correctly formatted and contains the necessary information. Atlas supports all geo formats, such as CSV, Shapefile, and GeoJSON.
- Verify Data: Once uploaded, verify that the data has been correctly interpreted by Atlas. Check for any errors or missing data.
Step 4: Style Layers
Layers are essential components of your map, representing different types of data.
Customize the appearance of each layer to make your map clear and informative. You can change colors, shapes, and labels.
Step 5: Customize the Map
- Basemap Selection: Choose a basemap that suits your needs. Atlas offers various base map options, such as satellite imagery, street maps, and topographic maps.
- Symbology: Customize the symbols used for points, lines, and polygons. Use different colors and shapes to distinguish between various types of data.
- Labels and Legends: Add labels to provide more context. Ensure that your map includes a legend to explain the symbols and colors used.
Step 6: Add Interactivity
Interactive maps provide users with more information and a better user experience.
Configure pop-ups to display additional information when users click on map features. For example, clicking on a point might show the name, address, and other details of a business.
Step 7: Analyze the Data
Atlas offers various tools for spatial analysis. Use these tools to gain insights from your data.
- Buffer Analysis: Create buffer zones around features to analyze proximity. For example, you can create a buffer around schools to see which areas fall within a certain distance.
- Heatmaps: Generate heatmaps to visualize density. This is useful for identifying hotspots, such as areas with a high concentration of incidents or businesses.
- Points-in-Polygon Analysis: Count points within polygons to understand distributions. For example, count the number of parks within each city district.
Step 8: Share and Export the Map
Once your map is ready, you can share it or export it for use in presentations or reports.
- Sharing Options: Atlas allows you to share your map with others via a link or embed it on a website. Ensure you set the appropriate sharing permissions.
- Exporting: Export your map in various formats, such as PNG, PDF, or interactive web maps. This is useful for including the map in documents or presentations.
Practical Applications
Urban Planning
Urban planners can create maps showing land use, infrastructure, and population distribution. These maps aid in making informed decisions about development and resource allocation.
Environmental Monitoring
Environmental scientists can create maps to monitor natural resources, track changes in land use, and analyze the impact of human activities on the environment.
Market Analysis
Businesses can create maps to analyze market trends, customer locations, and competitor distribution. This helps in planning marketing strategies and identifying new opportunities.
Public Health
Public health officials can create maps to track disease outbreaks, analyze healthcare facility distribution, and plan interventions. This helps in improving public health responses and resource allocation.
Tips for Effective Map Making
- Data Accuracy: Ensure your data is accurate and up-to-date. Incorrect data can lead to misleading maps and analyses.
- Clear Symbology: Use clear and distinct symbols and colors. Avoid cluttering the map with too many elements.
- User-Friendly Design: Design your map with the end-user in mind. Ensure it’s easy to understand and interact with.
- Iterate and Improve: Don’t hesitate to iterate on your map. Seek feedback and make improvements to enhance its usefulness.
Creating a map with Atlas is a straightforward process that involves uploading your data, creating layers, customizing the map, adding interactivity, and performing spatial analysis. Whether you’re working in urban planning, environmental monitoring, market analysis, or public health, Atlas provides the tools you need to create informative and interactive maps.
So, log in to Atlas, gather your data, and start making maps that bring your spatial data to life.