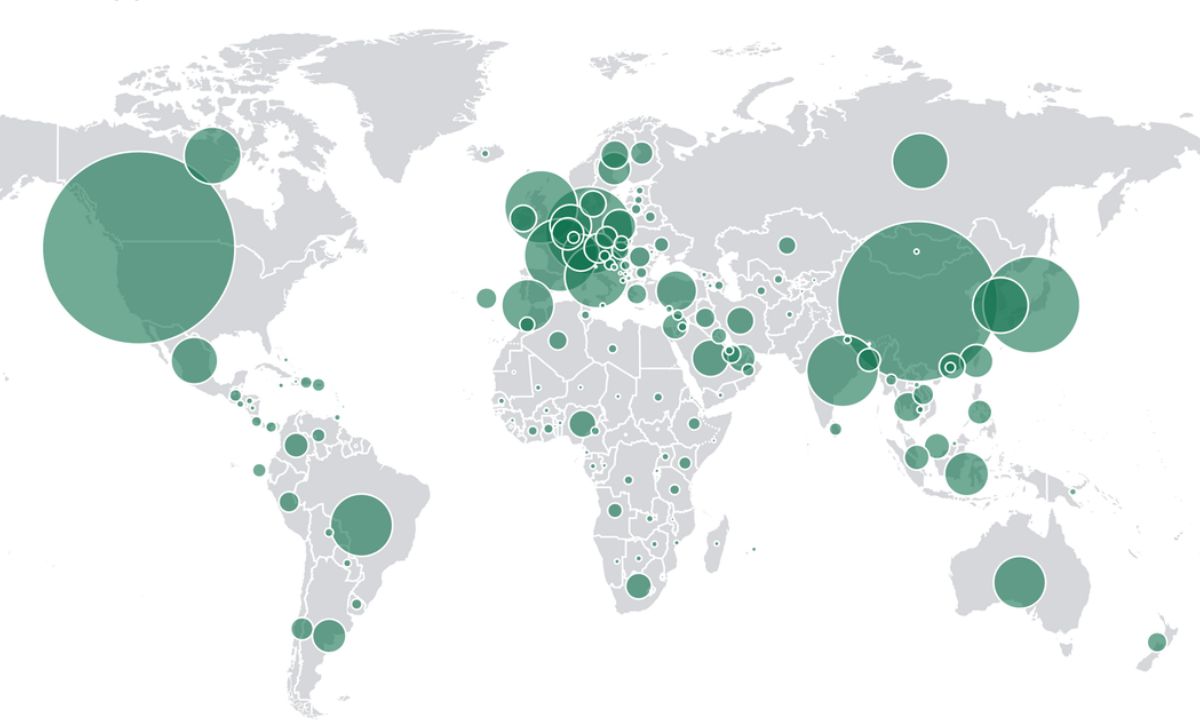
The World Bank stands as one of the most reputable sources for comprehensive global data, offering insights crucial for economic development, policymaking, and understanding international dynamics. This article will explore the scope, applications, and significance of World Bank data in various sectors, highlighting its essential role in today’s interconnected world.
Understanding World Bank Data
What is World Bank Data?
World Bank data is a collection of varied datasets and tools that provide detailed information on economic development indicators, demographic trends, and social metrics across the globe. These datasets are crucial for governments, researchers, policymakers, and organizations working in development fields.
Key Features:
- Global Reach: Covers a comprehensive range of countries, making it an essential resource for comparative analysis and global benchmarking.
- Variety of Indicators: Includes indicators on poverty, education, health, economy, infrastructure, and environmental factors.
- Open Access: Most data are freely accessible, fostering transparency and broad usability.
- Regular Updates: Data is updated regularly to reflect current trends and insights.
Major Components of World Bank Data
Economic Indicators
World Bank provides a robust set of economic indicators including GDP growth rates, industry outputs, trade balances, inflation rates, and employment statistics. These indicators are vital for assessing the economic health of nations and regions.
Social Metrics
Data on education, health, gender equality, and access to public services are crucial for understanding the social development level within countries. These metrics help in devising targeted interventions to uplift underdeveloped regions .
Environmental Data
With the rising importance of sustainability, World Bank’s environmental data, which includes information on carbon emissions, energy usage, and natural resources, assists in shaping policies around climate action and environmental protection .
Technological and Infrastructure Insights
Data on technological accessibility and infrastructure development, like internet penetration rates and road quality indexes, provide insights into a country’s capacity to support modern economic activities .
Work faster with spatial data
Easily import data, automate analysis and build spatial apps for the web, all within a single software.
Applications of World Bank Data
Policy Development
Governments utilize this data to formulate economic policies, allocate resources efficiently, and set development goals. By analyzing trends and patterns, policymakers can identify areas needing intervention and forecast future challenges .
Research and Academic Use
Researchers and academics often use World Bank data for studies related to economic development, social change, and comparative analyses among countries. This data helps in generating evidence-based recommendations and academic papers .
Business and Investment Decisions
Investors and corporations leverage World Bank data to understand market conditions and demographic trends, helping in informed decision-making regarding investments and business expansions .
NGO and Non-Profit Strategies
Non-Government Organizations (NGOs) and non-profits use this data to design programs aligning with actual needs, ensuring that resources are directed towards the most impactful areas .
Importance and Impact
Promoting Transparency and Accountability
World Bank data fosters transparency, ensuring that policymakers and leaders are working towards equitable development. Regular updates and open-access policies enable stakeholders to hold authorities accountable .
Driving Global Development and Collaboration
By providing a shared foundation of knowledge, World Bank data promotes international collaboration. Countries can exchange strategies for development, improve policies, and share successful models across borders .
Supporting Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs)
Through detailed metrics on poverty, education, and environmental sustainability, World Bank data supports progress toward the United Nations’ Sustainable Development Goals, offering a framework for monitoring and achieving these targets .
Challenges and Considerations
Data Reliability
While World Bank data is generally considered reliable, it is dependent on reporting from member countries, which can vary in accuracy and timeliness .
Technology and Accessibility Issues
In regions with limited technology infrastructure, accessing and utilizing World Bank data effectively can prove challenging .
Resource Limits
Not all data sets cover every detail required for specific analyses. Users may need to supplement World Bank data with other sources to gain a comprehensive view .
Tools and Platforms for Accessing World Bank Data
The World Bank offers various platforms for accessing its wealth of data, such as:
- World Bank Open Data: A platform offering free and open access to global development data.
- DataBank: An analysis and visualization tool that contains collections of time series data on various topics.
- Microdata Library: Includes datasets from World Bank surveys and censuses in developing countries.
These platforms enhance usability by integrating visualization tools, enabling users to effectively interpret and analyze data .
Work faster with spatial data
Easily import data, automate analysis and build spatial apps for the web, all within a single software.
How Atlas Enhances the Use of World Bank Data
Atlas, a modern GIS platform, is transforming how organizations and individuals access and analyze data, including comprehensive datasets from sources like the World Bank. Here’s how Atlas can empower you to leverage World Bank data more effectively:
Seamless Data Integration
Easy Import and Handling
With Atlas, importing World Bank datasets into your project is straightforward. Users can upload CSV or other compatible file formats directly into the platform. This feature eliminates the complexity often associated with data integration, allowing you to focus on analysis rather than data formatting issues.
Real-Time Collaboration
Atlas supports real-time collaboration, meaning teams can work on data simultaneously from different locations. This capability is particularly valuable when collaborating on international projects or when working with diverse datasets from sources like World Bank, fostering a more dynamic and cooperative environment.
Powerful Visualization Tools
Interactive Data Mapping
Atlas excels in turning raw data into intuitive and informative maps. Users can visualize World Bank data indicators such as GDP, population demographics, or environmental metrics, leveraging Atlas’s customizable maps. This visual capability is crucial for identifying patterns, trends, and correlations that might not be immediately apparent in raw data formats.
Customizable Visuals
Personalize your maps with custom colors, labels, and styles to highlight specific aspects of the World Bank data pertinent to your research or analysis. These customization options ensure that your maps effectively communicate your insights and align with your project’s needs.
Advanced Analytical Features
Spatial Analysis
Atlas offers sophisticated tools to perform spatial analysis, helping users extract deeper insights from World Bank datasets. Whether you need to analyze geographic distribution patterns or socio-economic impacts across regions, Atlas provides the capabilities necessary for comprehensive spatial assessments.
Scenario Building and Analysis
Users can create different scenarios using World Bank data to simulate potential policies or economic outcomes. This ability to forecast and model various situations makes Atlas a valuable tool for policy research and development, allowing stakeholders to make data-driven decisions.
Accessibility and Usability
Browser-Based Convenience
Atlas is completely browser-based, which means there's no need for extensive installations or maintenance. This ease of accessibility ensures that anyone with internet access can utilize its robust features without the hassle of software management.
User-Friendly Interface
The platform is designed to be user-friendly, even for those who may not have a deep background in GIS technology. This accessibility democratizes data analysis, allowing users from diverse fields to engage with and benefit from World Bank data efficiently.
Atlas stands as a powerful ally for users seeking to harness the full potential of World Bank data. With its comprehensive features, ease of use, and collaborative capabilities, Atlas transforms complex datasets into actionable insights, supporting better decision-making and fostering a deeper understanding of global development trends.