Shapefiles (SHP) are one of the most widely used file formats in Geographic Information Systems (GIS). They store spatial data like points, lines, and polygons, making them ideal for mapping geographic features. If you want to view and analyze shapefiles in Google Earth Pro, the process requires a few extra steps because Google Earth Pro works primarily with KML/KMZ files.
In this guide, we’ll explain what shapefiles are, how to convert them, and how to successfully import and visualize SHP files in Google Earth Pro.
What is a Shapefile (SHP)?
A shapefile (.shp) is a geospatial vector file format developed by Esri for storing location, shape, and attribute data. Shapefiles typically come as a set of related files, including:
- .shp: The main file containing geometry (points, lines, polygons).
- .shx: The index file.
- .dbf: The database file storing attribute data (names, values, etc.).
To import a shapefile into Google Earth Pro, you’ll first need to convert it to KML/KMZ format, which is natively supported.
Step-by-Step Guide: Importing SHP Files into Google Earth Pro
Here’s how you can convert and visualize your shapefiles in Google Earth Pro:
1. Prepare Your Shapefile
Ensure you have all the required shapefile components:
.shp,.shx, and.dbffiles.- Combine them into a single folder to keep the data organized.
If any of these files are missing, the shapefile may not work correctly.
2. Convert SHP to KML Using a Free Tool
Since Google Earth Pro doesn’t natively read SHP files, you must convert them to KML/KMZ format. Use a free GIS tool like QGIS or an online converter to do this.
Option 1: Convert SHP to KML with QGIS
- Download and install QGIS.
- Open QGIS and add your shapefile:
- Go to Layer > Add Layer > Add Vector Layer.
- Browse for your
.shpfile and click Open.
- Right-click the layer in the Layers Panel and choose Export > Save Features As.
- In the Format dropdown, select Keyhole Markup Language (KML).
- Set your file name and output location.
- Click OK to export.
Option 2: Convert SHP to KML Online
If you don’t want to install software, use free online tools like mapshaper.org or MyGeodata Converter.
- Upload your
.shpfile along with.shxand.dbf. - Select KML/KMZ as the output format.
- Download the converted KML file.
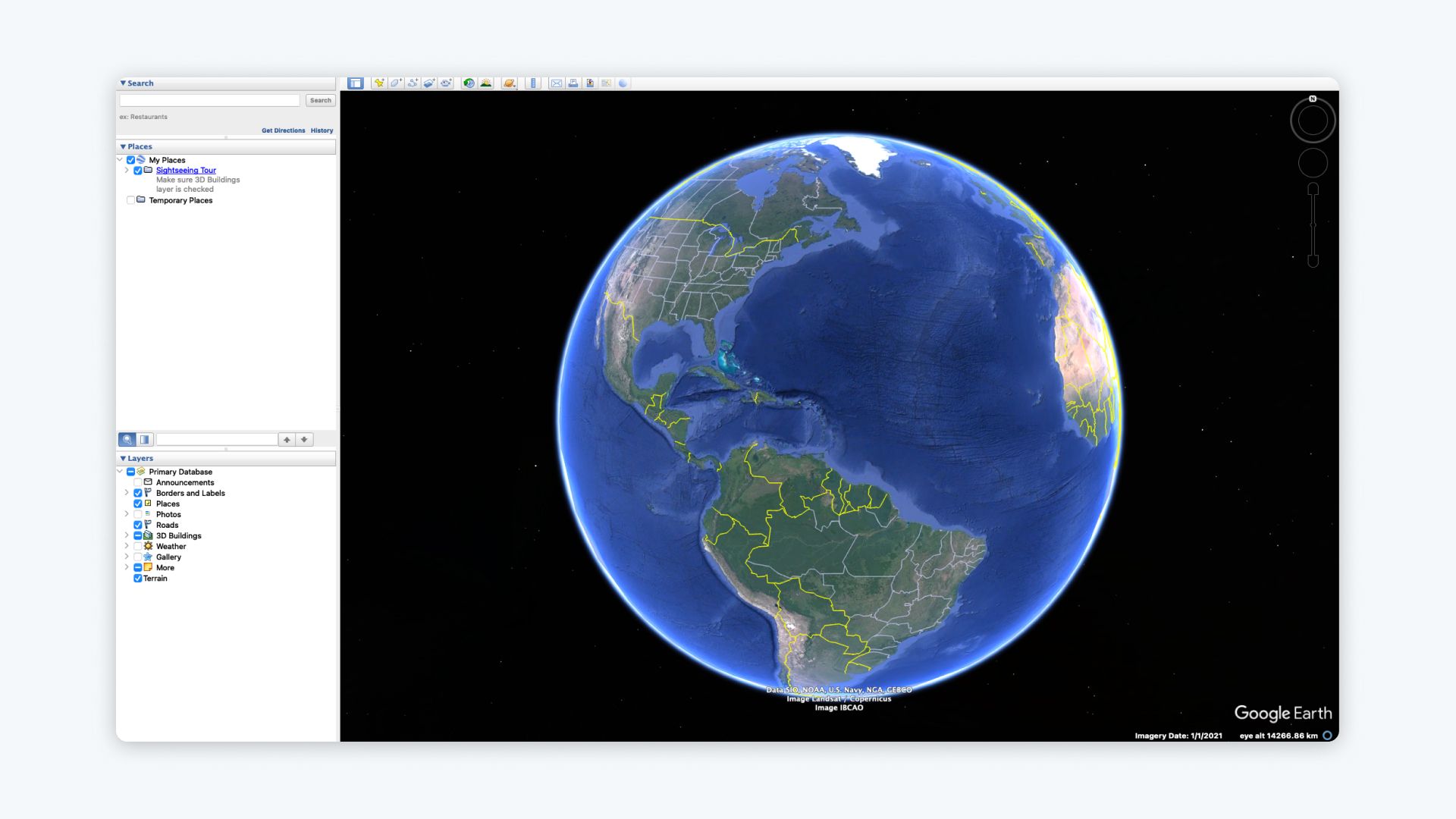
3. Import the KML/KMZ File into Google Earth Pro
Now that you have a KML file, follow these steps to import it into Google Earth Pro:
- Open Google Earth Pro on your desktop.
- Go to File > Open.
- Locate your converted KML/KMZ file and click Open.
- Your data will now appear in the Places panel and on the map.
4. Customize and Style Your Data
Once your shapefile data is imported, you can customize its appearance:
-
Change Icons and Colors:
- Right-click the imported KML file in the Places panel.
- Select Properties and adjust the Style, Color, and Labels.
-
Edit the Attributes:
- Edit pop-up descriptions to display attribute data like names or values.
-
Organize Data:
- Group features into folders or add sub-layers for better organization.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
1. Missing Attributes After Conversion
- Ensure you include the
.dbffile when converting the shapefile. This file contains attribute data.
2. Coordinate Issues
- Confirm that your shapefile uses the correct coordinate system (WGS84). Google Earth Pro requires latitude and longitude in WGS84 format.
3. File Import Errors
- Double-check that the KML file was exported correctly without errors.
- Use free tools like mapshaper.org to validate and simplify your file if it’s too large.
Why Import SHP Files into Google Earth Pro?
Shapefiles are widely used for mapping and spatial analysis. Importing them into Google Earth Pro allows you to:
- Visualize Complex Data: Display points, lines, and polygons on an interactive 3D globe.
- Share Results: Export KML files for presentations, reports, or sharing with clients.
- Analyze Locations: Use Google Earth’s tools to measure distances, compare data, or view historical imagery.
Common use cases include:
- Urban Planning: Visualize zoning boundaries or infrastructure layouts.
- Environmental Analysis: Map protected areas, rivers, or forest cover.
- Field Surveys: Analyze GPS survey data over satellite imagery.
Need Advanced Mapping Capabilities? Try Atlas
While Google Earth Pro works well for basic visualization, tools like Atlas provide advanced features for teams and professionals:
Why Choose Atlas?
- Native SHP Import: Upload and visualize shapefiles directly without conversion.
- Advanced Customization: Easily style layers, adjust colors, and edit attributes.
- Real-Time Collaboration: Work with teammates on the same map from anywhere.
- Interactive Features: Add pop-ups, filters, and legends to make your map dynamic.
- Browser-Based: No downloads or installations—just log in and start mapping.
Atlas simplifies geospatial workflows, especially for teams needing real-time collaboration and professional outputs.
Final Thoughts
While Google Earth Pro doesn’t natively support SHP files, converting them to KML/KMZ allows you to visualize shapefile data effectively. Tools like QGIS or online converters make the process quick and accessible.
If you need a platform that directly supports SHP imports and provides more advanced tools, consider using Atlas. With its intuitive interface and collaborative features, Atlas takes your mapping to the next level. Sign up for Atlas and start exploring your shapefiles today!