March was big. We ran our first-ever Launch Week and dropped five major features. After months of building, we rolled out our biggest updates yet — making it easier to automate workflows, build mobile-friendly apps, and collect spatial data from anyone.
Let's dive in.
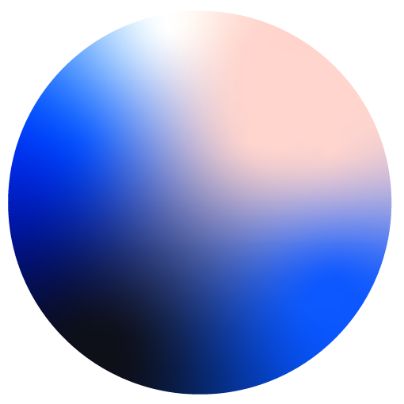
Workflows
Workflows let you automate complex geospatial tasks without code. Build sequences of filters, analyses, and logic using a visual interface. Perfect for processes like site selection or coverage analysis. You design the steps once and reuse them whenever needed. Workflows save time and reduce manual work, especially when analyzing large datasets or running routine checks.
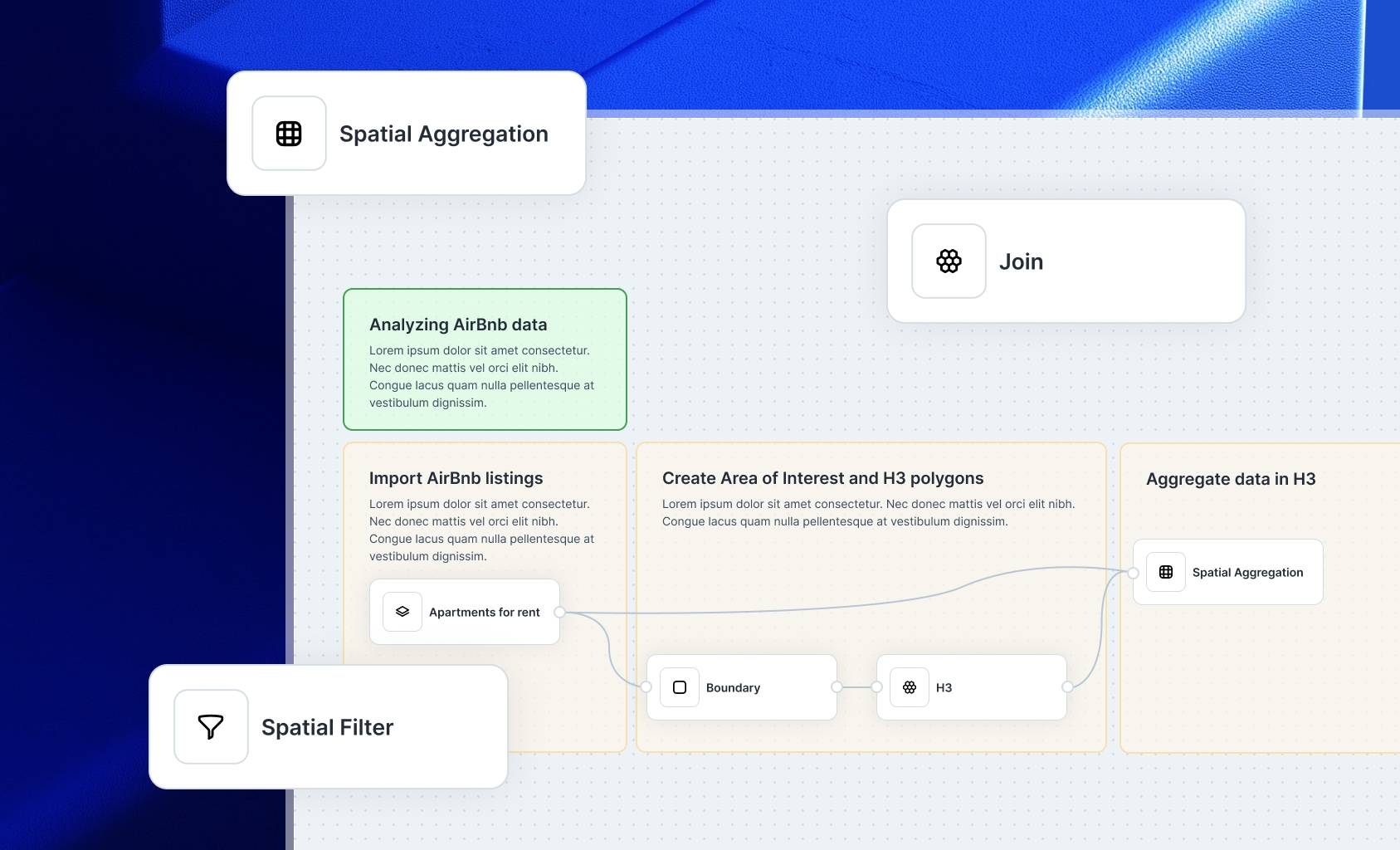
Forms
Forms allow you to collect geospatial data from anyone through a public link. Use a no-code builder to create the form, and users can submit a point or shape with associated information. You then review, approve, or reject the submission. It’s ideal for citizen feedback, issue reporting, or field data collection.
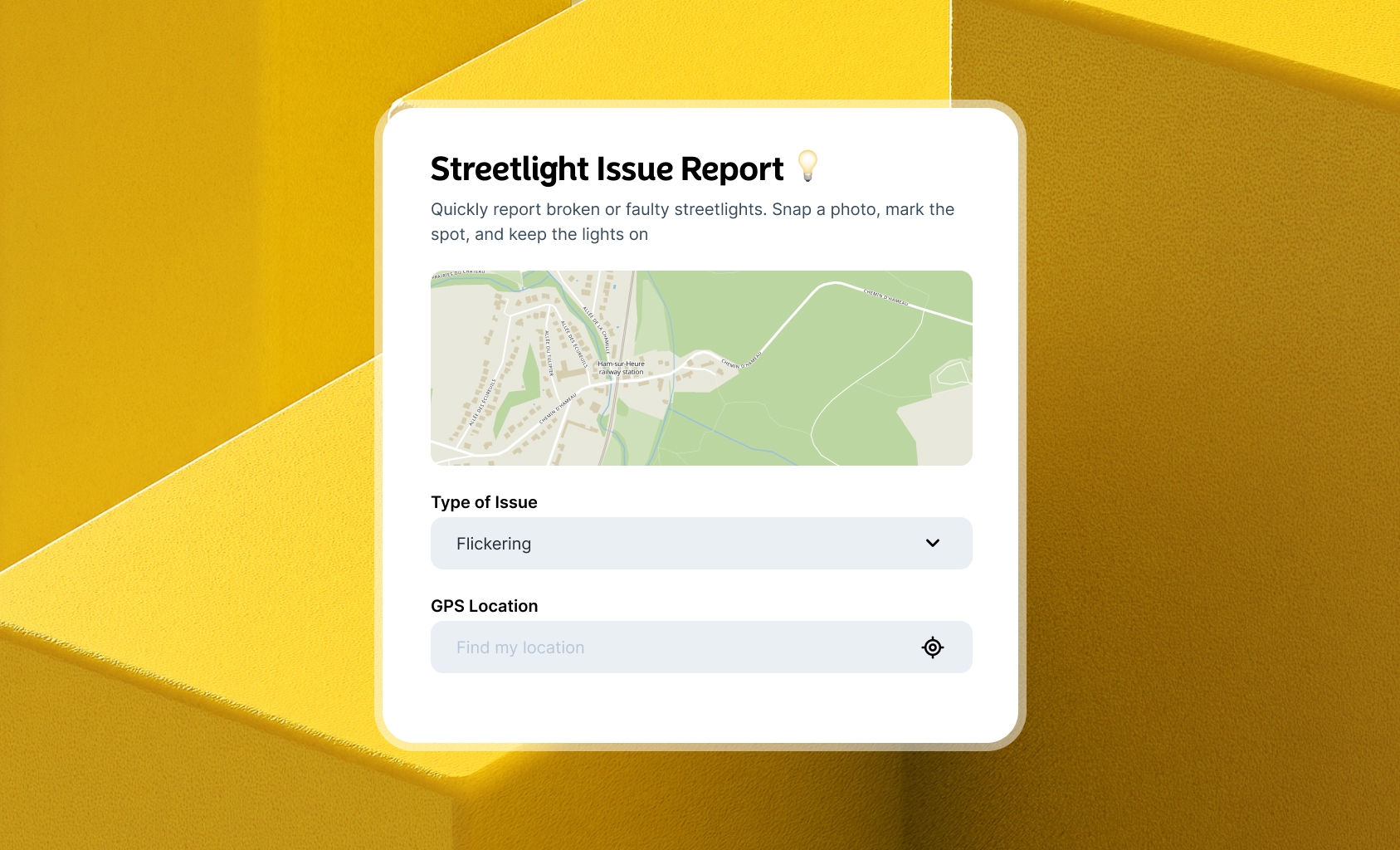
Mobile Builder
You can now customize how your maps and apps look on mobile. The Builder supports mobile layouts, allowing you to tailor the user experience for phones and tablets. Add a dedicated mobile menu, adjust components, and preview everything in real time. This means you can launch fully responsive spatial applications that work great in the field, for public users, or any mobile-first scenario — straight from the same place you already build your desktop apps.
Relations
Relations let you connect datasets — whether they have geometry or not. You can now link tables to each other or to spatial layers, creating powerful lookups across your data. This makes it easy to bring in related information, enrich datasets, or build complex views that combine spatial and tabular insights.
FeatureServer Support
Atlas now supports importing from ESRI FeatureServer. Pull in live data streams directly from your existing ESRI infrastructure and keep your maps automatically updated. This is great for connecting to existing systems without having to export and re-upload data manually. Whether you’re using ESRI for field data or base layers, now you can easily connect and display those layers in Atlas.
Wedge Buffer Analysis
Wedge Buffer lets you draw directional buffers using a distance and angle. It’s perfect for modeling sight lines, impact zones, or areas affected in a specific direction. Choose where the buffer starts, set the radius and angle, and the result gives you a targeted spatial zone. This tool is ideal for planning, safety checks, and visualizing directional influence in your maps.
New Bounds Selector
We’ve made it easier to select the bounds for any operation involving an Area of Interest (AOI). Whether you’re fetching data, or setting up a workflow — this new selector helps you define spatial bounds faster and with fewer clicks. The improved interface makes it clear what area you’re working within and ensures you only get the data you need.
H3
You can now run H3 analysis directly in Atlas. Generate hexagonal grid tiles over your data by selecting a resolution and method. H3 makes it easy to standardize spatial patterns, summarize data, and compare across regions. It’s great for density analysis, clustering, or just organizing your data spatially.